Last Update: 26th Jan 2025
Periodic extreme rainfall in a warmer climate due to stronger convectively-coupled waves
We find a new phenomenon: Precipitation in tropical convective regions will transition to a ~10-day periodic oscillation with a ~100 mm/day magnitude in a 5 – 10 K warmer climate. This transition occurs in both GCM and idealized cloud-resolving model simulations, and can be explained by the intensification of large-scale convectively-coupled waves under global warming.
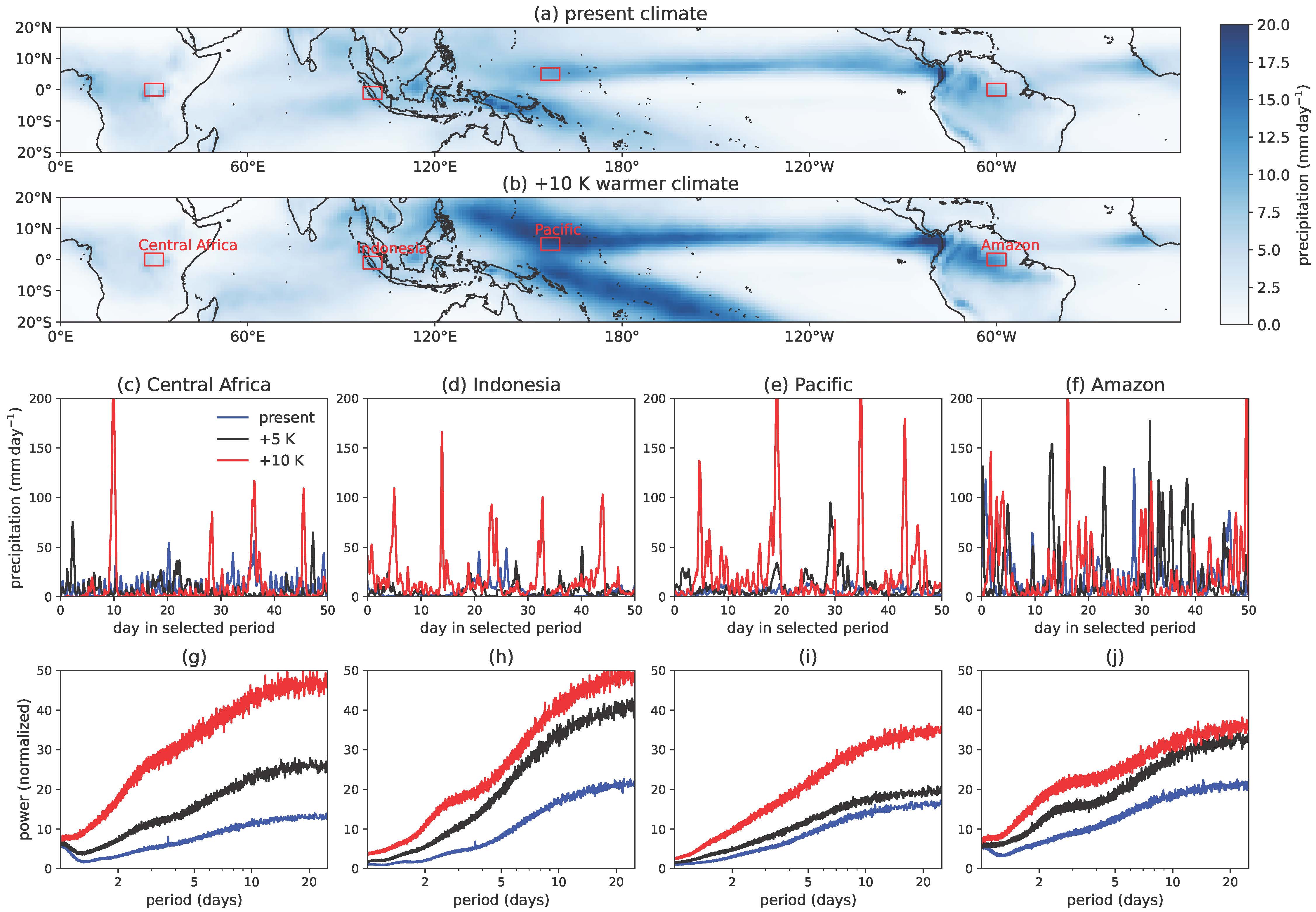
Collaborators: Yi Zhang, Stephan Fueglistaler, Guy Dagan
Weakening of tropical free tropospheric temperature gradients with global warming
The weak temperature gradients (WTG) in the tropical free troposphere due to the vanishing Coriolis force near the equator is fundamental to tropical atmospheric dynamics. Here we demonstrate that the weak temperature gradients will be even weaker in the future, which is explained by the slow-down of tropical circulation under global warming.
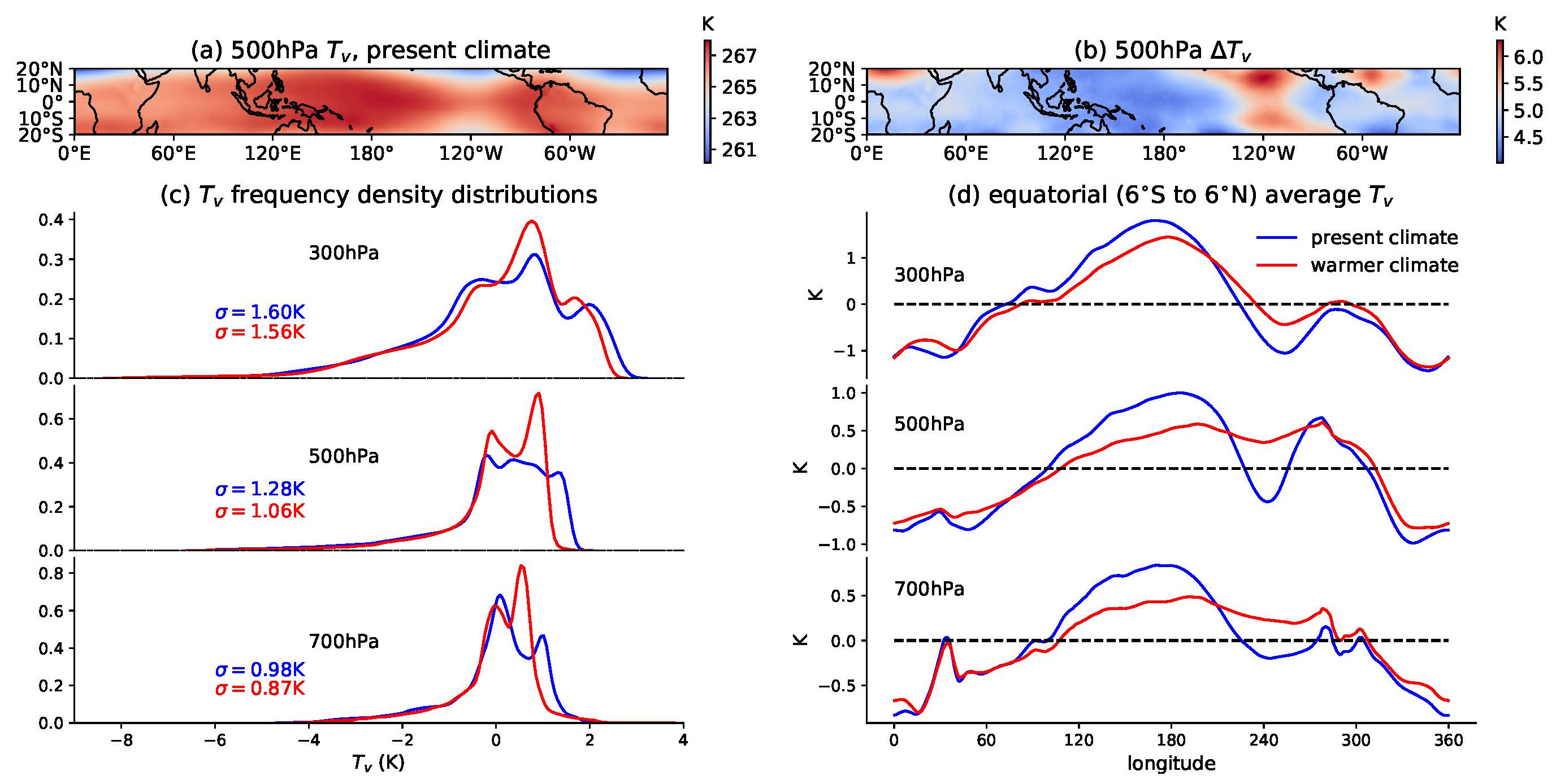
Collaborators: Yi Zhang, Stephan Fueglistaler
See the video and paper in Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences.
The SST pattern effect on OLR: the role of large-scale convective aggregation
Previous studies show that the west-east SST gradient in tropical Pacific affects shortwave cloud radiative effect by modulating boundary layer inversion strength and low cloud amount. Here we argue that the SST gradient also affects OLR by modulating the strength of large-scale convective aggregation (i.e. the width of the convective area). This mechanism strongly slows down global warming in the 1980-2010 period which has a La-Nina-like SST warming pattern.
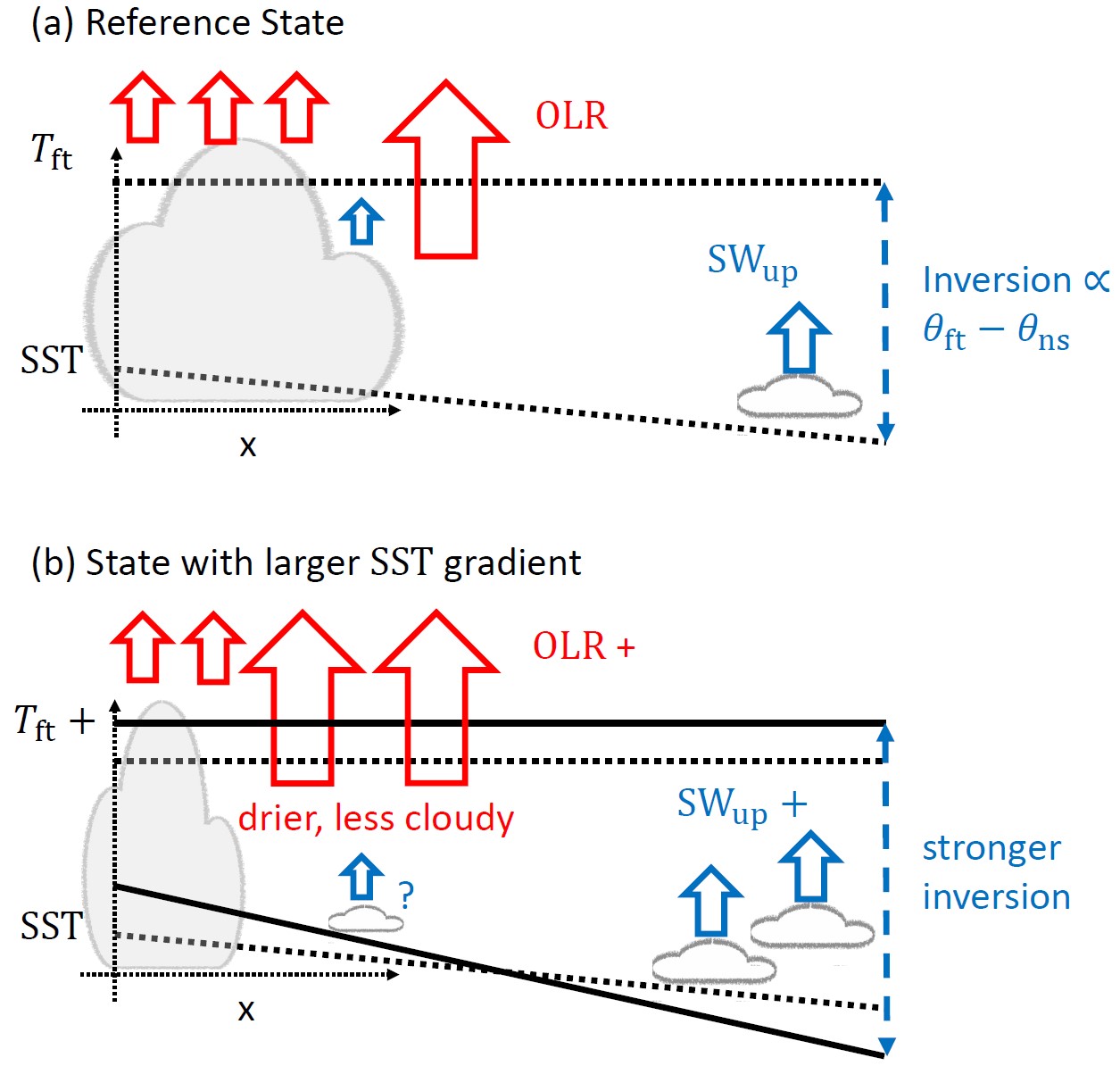
Collaborators: Stephan Fueglistaler, Bosong Zhang, Chenggong Wang
See the video and paper in Geophysical Research Letters.
The non-additivity problem in the SST Green’s Function approach
OLR responses to SST perturbations at different locations are not additive, because large-scale convection aggregation responses are not additive. This can be ultimately explained by non-linear tropical atmospheric dynamics.
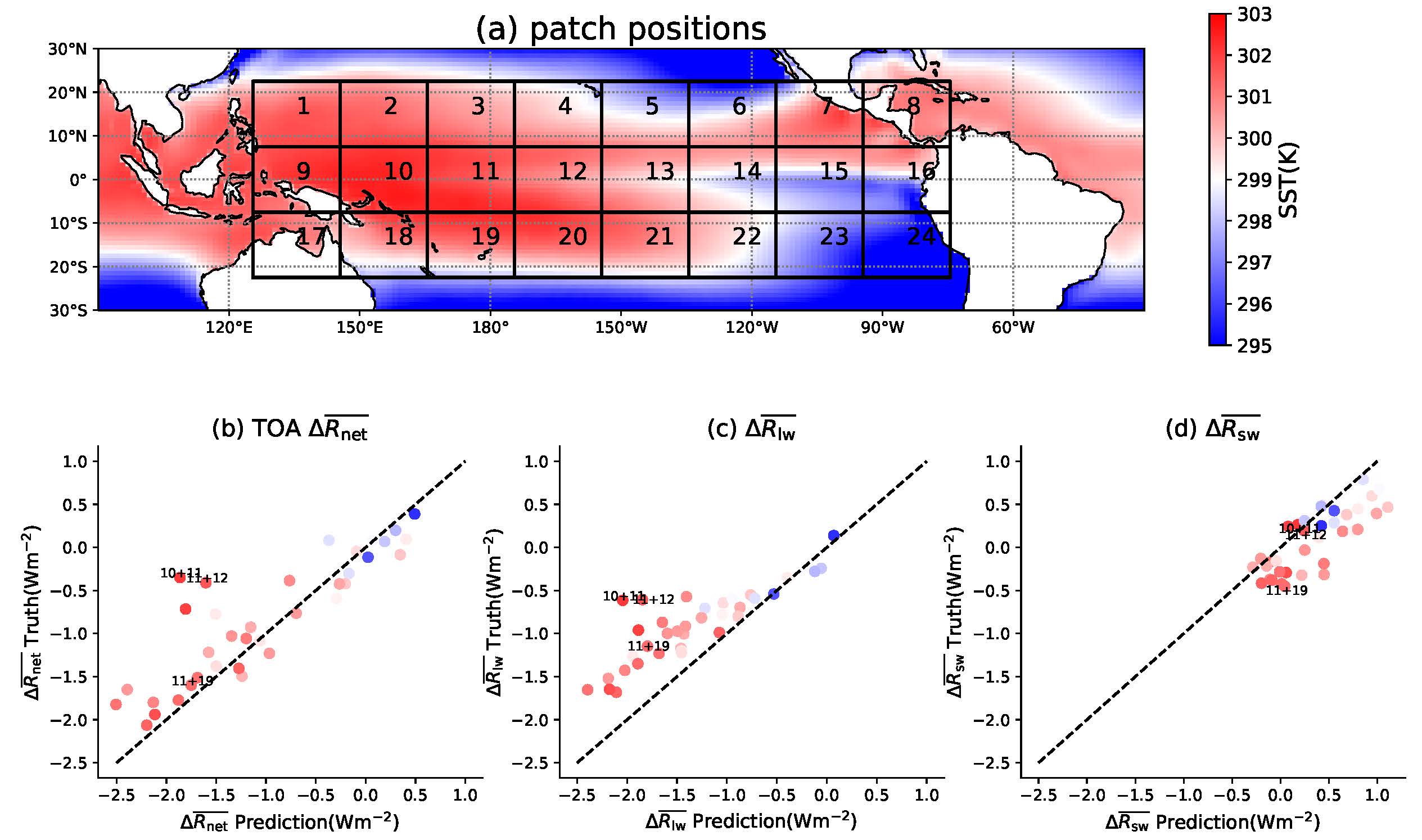
Collaborators: Stephan Fueglistaler, Bosong Zhang, Chenggong Wang
See the video and paper in Journal of Climate.
Reinforcement Learning for Geoengineering
Solar Geoengineering via stratospheric sulfate aerosol injection can be thought as an optimization problem. In this research we optimize the temporal and spatial distribution of aerosol injection by coupling reinforcement learning (RL) to a GCM online. Our results provide a first proof-of-concept that RL can identify effective and promising strategies to prevent further climate change or revert already-existing climate change.
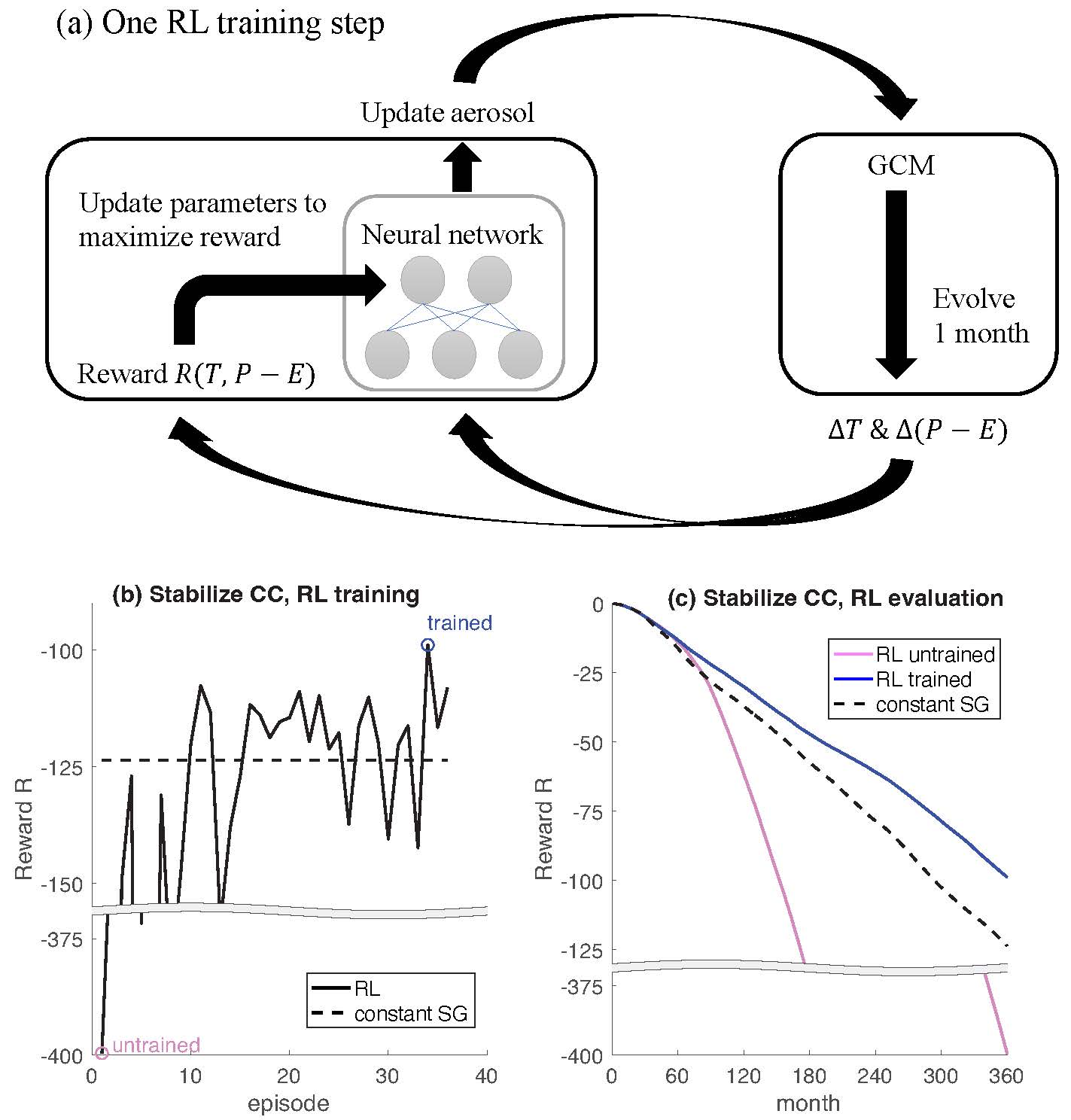
Collaborators: Daniel Koll (my bachelor thesis advisor), Nicholas Lutsko, Janni Yuval
See the paper in JGR Atmospheres.
Conditional mean temperature tendency decomposition
This research proposes a conditional mean temperature tendency decomposition framework that tells us what processes drive temperature towards or away from extremes at every temperature percentile, which is very useful for extreme events studies. It tells us that horizontal temperature advection drives temperatures toward more extreme values over most land in the midlatitudes, but dampens temperature anomalies in some coastal summer monsoon regions, where extreme temperatures result from other processes. This is my 2021 summer research, advised by Professor Marianna Linz at Harvard University and Professor Gang Chen at UCLA. The research paper is published in Journal of Climate.
Asymmetry of temperature series
Daily mean temperature series at the mid-latitudes usually have an asymmetric property: They cool rapidly and warm gradually. This research shows that such temperature asymmetry is due to the asymmetry of frequency and intensity between cold and warm fronts: In North China Plain, for example, cold fronts are stronger and more frequent than warm fronts, so daily mean temperature series cools rapidly and warms gradually. This is my undergraduate research in 2021, advised by Professor Zuntao Fu at Peking University. The research paper is published in International Journal of Climatology.
